

An amorphous metal transformer (AMT) is a type of energy efficient transformer found on electric grids.The magnetic core of this transformer is made with a ferromagnetic amorphous metal. The typical material (Metglas) is an alloy of iron with boron, silicon, and phosphorus in the form of thin (e.g. 25 µm) foils. These materials have high magnetic susceptibility, very low coercivity and high electrical resistance. The high resistance and thin foils lead to low losses by eddy currents when subjected to alternating magnetic fields. On the downside amorphous alloys have a lower saturation induction and often a higher magnetostriction compared to conventional crystalline iron-silicon electrical steel .
Core loss and copper loss
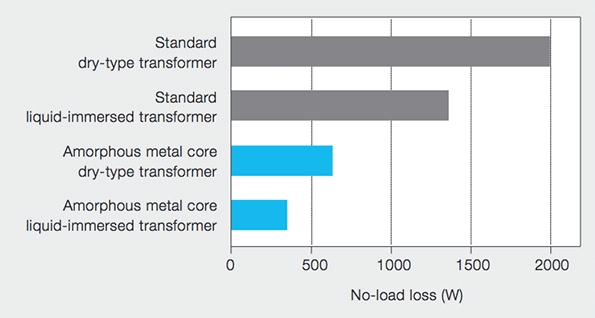
In a transformer the no load loss is dominated by the core loss. With an amorphous core, this can be 70–80% lower than with traditional crystalline materials. The loss under heavy load is dominated by the resistance of the copper windings and thus called copper loss. Here the lower saturation magnetization of amorphous cores tend to result in a lower efficiency at full load. Using more copper and core material it is possible to compensate for this. So high efficiency AMTs can be more efficient at low and high load, though at a larger size. The more expensive amorphous core material, the more difficult handling and the need for more copper windings make an AMT more expensive than a traditional transformer.
Advantages and disadvantages
More efficient transformers lead to a reduction of generation requirement and, when using electric power generated from fossil fuels, less CO2 emissions. This technology has been widely adopted by large developing countries such as China and India where labour cost is low. AMT are in fact more labour-intensive than conventional distribution transformer, a reason that explain a very low adoption in the comparable (by size) European market. These two countries can potentially save 25–30 TWh electricity annually, eliminate 6-8 GW generation investment, and reduce 20–30 million tons of CO2 emission by fully utilizing this technology



